Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation
- Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Calculator
- Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Calculator
- Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Chart
By Duncan Epping, Principal Architect, VMware
Yesterday I received a question on twitter:

The cluster has two host nodes, each with 24 GB of RAM and 2 Quad Core Procs. Host reserves are all on the defaults. So 512 KB of RAM is reserved for the hosts and 20 percent CPU. The Slot size is calculated by the CPU and Memory Reservations at the individual Virtual Machine level in the whole cluster, the largest VM's CPU and Memory reservation determines the slot size. For more information on the slot size calculations on the different versions.
Hi, to settle an argument in the office, if no reserves are in place, does number of vCPU’s affect slot size in vSphere 4? Thx 🙂
First of all, what is a slot? The availability guide explains it as follows
A slot is a logical representation of the memory and CPU resources that satisfy the requirements for any powered-on virtual machine in the cluster.
In other words a slot is the worst case CPU and Memory reservation scenario for any given virtual machine in a cluster. This slot is used when Admission Control is enabled and “Host Failures Tolerates” has been selected as the admission control policy. The total amount of available resources in the cluster will be divided by the slot size and that dictates how many VMs can be powered on without violating availability constraints. Meaning that it will guarantee that every powered on virtual machine can be failed over.
As said this slot is dictated by the worst case reservation for CPU and Memory. Prior to vSphere 4.0 we used the number of vCPUs to determine the slotsize for CPU as well. But we do not use vCPUs anymore to determine the slot size for CPU. The slotsize for CPU is determined by the highest reservation or 256MHz (vSphere 4.x and prior) / 32MHz (vSphere 5) if no reservation is set.
However, vCPUs can have an impact on your slot… it can have an impact on your memory slotsize. If no reservation is set anywhere HA will use the highest Memory Overhead in your cluster as the slot size for memory. This is where the amount of vCPUs come in to play, the more vCPUs you add to a virtual machine the higher will your memory overhead be.
I guess the answer to this question is: For CPU the number of vCPUs does not impact your slotsize, but for memory it may.
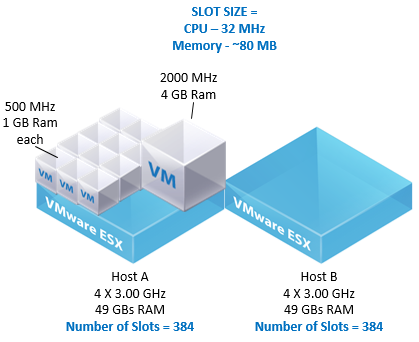
I’ve been receiving a lot of questions around slot sizes lately. Although I point everyone to my HA Deepdive post not everyone seems to understand what I am trying to explain. The foremost reason is that most people need to be able to visualize it; which is tough with slot sizes. Just to freshen up an outtake from the article:
HA uses the highest CPU reservation of any given VM and the highest memory reservation of any given VM. If there is no reservation a default of 256Mhz will be used for the CPU slot and the memory overhead will be used for the memory slot!

If VM1 has 2GHZ and 1024GB reserved and VM2 has 1GHZ and 2048GB reserved the slot size for memory will be 2048MB+memory overhead and the slot size for CPU will be 2GHZ.
Now how does HA calculate how many slots are available per host?
Of course we need to know what the slot size for memory and CPU is first. Then we divide the total available CPU resources of a host by the CPU slot size and the total available Memory Resources of a host by the memory slot size. This leaves us with a slot size for both memory and CPU. The most restrictive number is the amount of slots for this host. If you have 25 CPU slots but only 5 memory slots the amount of available slots for this host will be 5.
The first question I got was around unbalanced clusters. Unbalanced would for instance be a cluster with 5 hosts of which one contains substantially more memory than the others. What would happen to the total amount of slots in a cluster of the following specs:
Five hosts, each host has 16GB of memory except for one host(esx5) which has recently been added and has 32GB of memory. One of the VMs in this cluster has 4CPUs and 4GB of memory, because there are no reservations set the memory overhead of 325MB is being used to calculate the memory slot sizes. (It’s more restrictive than the CPU slot size.)
This results in 50 slots for esx01, esx02, esx03 and esx04. However, esx05 will have 100 slots available. Although this sounds great admission control rules the host out with the most slots as it takes the worst case scenario into account. In other words; end result: 200 slot cluster.
With 5 hosts of 16GB, (5 x 50) – (1 x 50), the result would have been exactly the same. To make a long story short: balance your clusters when using admission control!
The second question I received this week was around limiting the slotsizes with the advanced options das.slotCpuInMHz and/or das.slotMemInMB. If you need to use a high reservation for either CPU or Memory these options could definitely be useful, there is however something that you need to know. Check this diagram and see if you spot the problem, the das.slotMemInMB has been set to 1024MB.

Notice that the memory slotsize has been set to 1024MB. VM24 has a 4GB reservation set. Because of this VM24 spans 4 slots. As you might have noticed none of the hosts has 4 slots left. Although in total there are enough slots available; they are scattered and HA might not be able to actually boot VM24. Keep in mind that admission control does not take scattering of slots into account. It does count 4 slots for VM24, but it will not verify the amount of available slots per host.
To make sure you will always have enough slots and know what your current situation is Alan Renouf wrote an excellent script. This script reports the following:
Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Calculator
Example Output:
Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Calculator
Cluster : Production
TotalSlots : 32
UsedSlots : 10
AvailableSlots : 22
SlotNumvCPUs : 1
SlotCPUMHz : 256
SlotMemoryMB : 118
Vmware Cluster Slot Size Calculation Chart
My article was a collaboration with Alan and I hope you find both article valuable. We’ve put a lot of time into making things as straight forward and simplistic as we possibly can.